Hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are two distinct conditions that individuals with diabetes often encounter. These fluctuations in blood sugar levels can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being. In this blog post, we will delve into the differences between hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, their causes, symptoms, and essential management strategies.

Understanding Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia:
Hyperglycemia refers to high blood sugar levels, often caused by insufficient insulin, excessive carbohydrate intake, or stress. Hypoglycemia, on the other hand, is characterized by low blood sugar levels, usually resulting from too much insulin or not enough food intake. Both conditions require careful attention and timely management.
Recognizing the Symptoms:
Hyperglycemia symptoms may include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow wound healing. Hypoglycemia symptoms can manifest as shakiness, sweating, confusion, irritability, and in severe cases, unconsciousness. Understanding these distinct sets of symptoms is crucial for appropriate intervention.

Causes and Triggers:
Hyperglycemia can be triggered by missed insulin doses, illness, stress, or consuming high-carbohydrate foods. Hypoglycemia can occur due to excess insulin, increased physical activity, delayed or missed meals, or alcohol consumption. Being aware of potential triggers can help you manage your blood sugar levels more effectively.
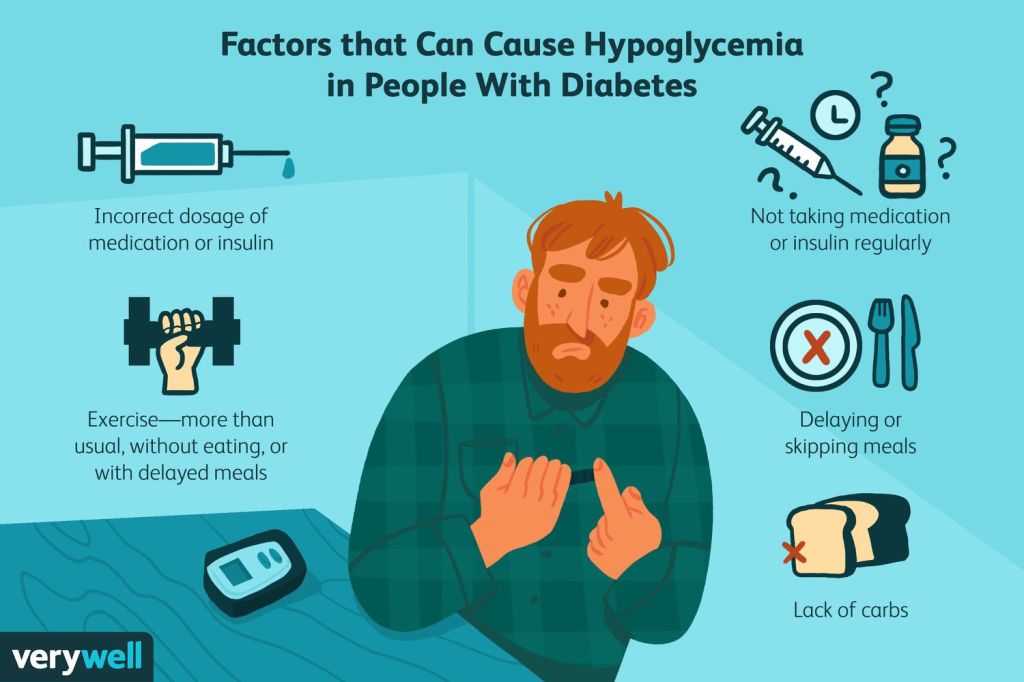
Prevention and Management:
Preventing hyperglycemia involves adhering to your diabetes management plan, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, following a balanced diet, and maintaining an active lifestyle. To prevent hypoglycemia, it’s important to monitor your blood sugar, coordinate insulin dosages with your meals and activities, and have a plan for treating low blood sugar episodes with fast-acting carbohydrates.


Conclusion:
Hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are two sides of the same coin in diabetes management. Understanding the differences between these conditions, their triggers, and how to prevent and manage them is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and overall health. Regular communication with your healthcare team, consistent self-monitoring, and being prepared for potential episodes are essential components of effective diabetes care.

Remember that your journey with diabetes is unique, and staying informed about both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia empowers you to navigate the challenges with confidence.
With care and support,
DiabeticGirl
Leave a comment